Mikroskopis Urine
Evaluasi
mikroskopis dari sedimen urin seringkali menghasilkan informasi berharga bgi
dokter untuk membuat diagnosis yang lebih spesifik atau penilaian terapi
yang tidak bisa didapat hanya dengan pemeriksaan fisikokimia urin.
Prosedur
urine mikroskopis cukup sederhana dan memerlukan sedikit peralatan, yaitu,
centrifuge, tabung sentrifus, mikroskop binocular,
object + cover glass., dan sarana untuk memastikan bahwa prosedur
QA yang ketat telah diikuti. Konstituen dalam sedimen bisa
bervariasi, dan interpretasi akurat sering tergantung pada pengalaman
sebelumnya. Beberapa praktisi telah menganjurkan untuk tidak dilakukan
pemusingan air seni ketika melakukan pemeriksaan mikroskopis (praktik umum di
Inggris), Penulis mengikuti praktek standar di Amerika Serikat yaitu dengan
Sentrifugasi 10 atau 12 mL urin selama 5 menit dan gaya sentrifugal
relatif (RCF) 400 sampai 500 (4.000-5.000 rpm) untuk memperoleh sedimen
di bagian bawah tabung centrifuge. Selanjutnya,
sediment yang diperoleh dicampur dengan air kencing sehingga alikuot
dapat dituang dan dilihat dengan mikroskop
Sebagai contoh, jika volume awal urin 12 mL dan volume supernatan
yang tersisa setelah sentrifugasi urin adalah 1 mL, berarti
konsentrasi sedimen yang dihasilkan adalah 1 : 12. Dengan
mengetahui volume konstan urin yang digunakan, unsur-unsur sedimen
yang dilihat dapat dihitung berdasarkan volume (yakni, angka per
mililiter) bukan sebagai angka per lapangan mikroskopis. Penggunaan
sistem standar untuk pemeriksaan ini memungkinkan konsistensi jauh lebih besar
dalam pelaporan hasil.
Sentrifugasi
pada RCF 400 sampai 500 selama 5 menit menghasilkan sedimen terkonsentrasi di
mana semua unsur dapat dengan mudah ditemukan dan tidak
terdistorsi. Centrifuge modern dapat menyesuaikan putaran per
menit (rpm) tapi tidak untuk RCF. Rumus berikut mempertimbangkan
radius kepala centrifuge untuk menentukan RCF = 1,118 × 10 -3 × radius
kepala sentrifus (dalam cm × rpm 2)
Sedimen
normal urin
Pengamatan sedimen
tergantung pada "mata yang baik," tahu apa yang ada dalam urin
normal, dan bisa mendefinisikan secara akurat dan membandingkan antara
bentukan normal dengan abnormal. Munculnya beberapa partikel atau elemen
dalam urin mungkin normal. Ini dapat berupa sel-sel darah, sel-sel yang
melapisi saluran kencing, sekresi kelenjar lendir, partikel protein silinder
yang telah terbentuk di nefron (gips), kristal yang terbentuk dalam urin, dan
sel asing (misalnya, spermatozoa pada seorang wanita), mikroorganisme, atau
kontaminan. Masing-masing konstituen akan dibahas secara terpisah.
TABEL
1. Konstituen SEDIMEN URINE NORMAL
Sel
Kristal
Gips
Lainnya
Sel darah
Asam urin
Hening Lendir
Merah
Amorf
Granular
Sperma
Putih
Asam urat
Mikroorganisme
Sel epitel
Netral urin
Bakteri
Skuamosa
Kalsium
oksalat
Jamur
Urothelial
Hippuric
asam
Kontaminan
Renal
tubular
Alkaline
urine
Serat
Triple fosfat
Serbuk sari
Amonium biurate
Kalsium karbonat
Sel darah
Eritrosit
(sel darah merah) dan leukosit (sel darah putih) dapat ditemukan dalam jumlah
kecil di sedimen normal. Sel-sel ini dapat melewati glomerulus dan
masuk ke aliran urin. Penghitungan sel-sel ini selama periode waktu, misalnya
12 jam, sekarang jarang dilakukan karena perbedaan
ekskresi selular dari orang ke orang dan adanya kesulitan yang
berhubungan dengan pengumpulan urin dan teknik penghitungan (menggunakan
hemositometer Addis count) . Seorang individu sehat dapat melepaskan sebanyak
750.000 1.750.000 sel darah merah dan leukosit melalui urine dalam 12 jam.
Sel darah
merah
Pada sedimen
urin normal sejumlah 0 - 5 sel eritrosit per LP dapat ditemukan
Jumlah lebih besar dari lima per LP harus diselidiki secara
menyeluruh dan penyebab hematuria harus dicari. Mikroskopik sel
darah merah terlihat mirip dengan yang ditemukan dalam darah perifer, yaitu
dobel disk cekung yang memiliki warna oranye samar pucat yang
menyatakan kadar hemoglobin mereka ( Gambar .2. ). Dalam urin hipertonik,
sel darah merah mungkin crenated dan dalam urin hipotonik mereka mungkin
membengkak, menjadi bola, dan, pada waktunya, pecah, hanya menyisakan
membran atau sel "hantu" yang terlihat seperti
tetesan kecil minyak. Tetesan minyak dapat dibedakan dari sel darah
merah berdasarkan ukurannya yang bervariasi, tidak adanya hemoglobin, dan
berbentuk bulat.
GAMBAR 1 sel darah merah. (Sel darah merah)
dan bakteri dalam sedimen urin. Tampak sebaran sel darah merah dan bentuk
bacillary. Dua leukosit juga tampak di tengah lapangan pandang. (
mikroskop cahaya, × 160.)
GAMBAR
2. Neutrofil
PMN dan sel-sel darah merah dalam urin. Tampak jelas sel
darah merah bikonkav dan inti multilobe serta sitoplasma granular dari
neutrofil. Beberapa sel darah merah sedikit crenated. ( mikroskop, ×
200.)
Leukosit
Leukosit
sering ditemukan pada sedimen urin normal, tetapi sedikit dan tidak boleh
melebihi lima per LP Walaupun semua jenis WBC yang muncul dalam
darah perifer juga dapat ditemukan dalam urin (yaitu, limfosit, monosit,
eosinofil), saat ini sel yang paling umum adalah PMN. PMN memiliki fungsi
fagositosis, motil secara aktif, dan bergerak secara ameboid dengan
pseudopodia. Leukosit ukuran diameter 10 sampai 20 pM, . PMN dalam urine
dapat segera diketahui karena inti multisegmented
dan sitoplasma granular.
Pewarnaan sedimen
memungkinkan pengamat untuk mengidentifikasi PMN lebih mudah karena inti
multilobe tampak jelas dan dapat mengurangi kebingungan dengan sel
nonleukocytic, seperti sel-sel RTE. Pewarnaan Wright atau Giemsa
merupakan sarana akurat mengidentifikasi berbagai leukosit lainnya,
seperti limfosit dan eosinofil
Sel epitel
Urin normal
berisi tiga varietas utama sel epitel: tubular ginjal, transisi (urothelial),
dan skuamosa Sel-sel ini melapisi saluran kemih, tubulus dan
nefron. Beberapa fitur yang membedakan masing-masing jenis sel
epitel dapat dilihat pada table 2.
TABEL
2. SEL Epitel DARI URINE
Renal Tubular Urothelial
Skuamosa
Asal
Nefron
Pelvis ginjal, saluran kencing,
pekencingan terminal
kandung kemih,
vagina
pekencingan proksimal
Ukuran (pM)
15-25
20-30
30-50
Bentuk
Polyhedral
Polyhedral,
rata
"Kecebong",
bulat
Lainnya
Mikrovili jika dari
tubulus proksimal
Sel Epitel
Renal Tubular
Sel RTE
jarang ada dalam sedimen urin orang normal (nol sampai satu per
lima LP). Bila ada, biasanya dalam bentuk tunggal tetapi juga dapat
ditemukan berpasangan. Jika ada batas microvillus, berasal
dari tubulus proksimal. Identifikasi imunohistokimia dengan
cara pewarnaan fosfatase asam dapat dilakukan bila diperlukan, karena sel-sel
RTE memiliki kandungan enzim intraselular yang tinggi.
Bentuk paling sering adalah
polyhedral, tetapi mungkin agak datar, menunjukkan bahwa mereka
berasal dari lengkung Henle. inti mereka biasanya eksentrik tetapi mungkin
sentral; tampak jelas seperti bola dengan nukleolus jika tidak ada
perubahan autolytic.
RTE sel
biasanya ditemukan dalam air seni karena proses pembaharuan dan
regenerasi sel tubular. Pada biopsi ginjal, sel-sel lapisan tubular sering
menunjukkan aktivitas mitosis, sel-sel yang lebih tua lepas ke aliran urin dan
dapat dilihat dalam sediment. Jenis regenerasi sel terjadi
pada nefron proksimal daripada distal,.
Sel Epitel
Transisi
Sel ini
(juga disebut sel urothelial) merupakan lapisan epitel pada sebagian besar
saluran kemih dan sering tampak di sedimen (nol sampai satu per LP). Bentuknya
bertingkat-tingkat dan biasanya beberapa lapisan sel tebal. Ada
tiga bentuk utama: bulat ( Gambar 3. ), polyhedral, dan
"kecebong." , sel Transisi memiliki karakteristik yang khas yaitu
mudah menyerap air dan dengan demikian membengkak sampai dua kali ukuran
aslinya.. Sel transisi Polyhedral sulit dibedakan dari sel RTE jika mereka
tidak memiliki permukaan microvillus dan memiliki inti di pusat. Sitoplasma sel
transisional tidak mengandung jumlah besar fosfatase asam. Sel urothelial
berbentuk kecebong sering tampak dalam urin. Mereka mungkin berasal dari lapisan
pertengahan epitel transisi. Sel Transisi kecebong muncul
dalam kelompok-kelompok atau pasangan, serta tunggal, inti biasanya di
pusat, dan mereka memiliki sitoplasma berbentuk fusiform
Peningkatan jumlah sel Transisi dalam urin
biasanya menandakan inflamasi pada saluran kemih.

GAMBAR
3) Sel
Transisi. (panah) dan sel darah putih serta sel darah merah dalam urin.
Perhatikan bentuk bola dan inti di pusat sel ini. ( mikroskop cahaya, ×
160.)
Sel epitel
skuamosa
Sel epitel
skuamosa adalah yang termudah dari semua sel epitel, dan mudah dikenali
dan sering dijumpai dalam urin karena bentuknya yang besar, datar, (
Gambar 4. ). Spesimen urine porsi tengah
paling baik digunakan. Sejumlah sel skuamosa dalam
urin dari seorang pasien wanita biasanya menunjukkan kontaminasi vagina.
GAMBAR
4. Sekelompok
sel epitel skuamosa dalam urin. Sel-sel yang besar dan datar dan memiliki
beberapa butiran dalam sitoplasma mereka. Inti di pusat besarnya sekitar
ukuran limfosit . ( mikroskop cahaya, × 160.)
Kristal
Pembentukan
kristal berkaitan dengan konsentrasi berbagai garam di urin yang
berhubungan dengan metabolisme makanan pasien dan asupan cairan
serta dampak dari perubahan yang terjadi dalam urin setelah koleksi sampel
(yaitu perubahan pH dan suhu, yang mengubah kelarutan garam dalam air seni dan
menghasilkan pembentukan kristal). Karena ginjal memainkan peran utama dalam
ekskresi metabolit dan pemeliharaan homeostasis, produk akhir dari metabolisme
ditemukan dalam konsentrasi tinggi dalam urin, dan ini cenderung untuk
mengendapkan kristal ( 10 ). PH urin normal bervariasi dan
beberapa kristal dikaitkan dengan pH asam dan basa. atau netral, dan siswa
dengan baik disarankan untuk menyadari berbagai bentuk morfologis dan
karakteristik mereka. Beberapa jenis kristal ada yang dianggap
abnormal.
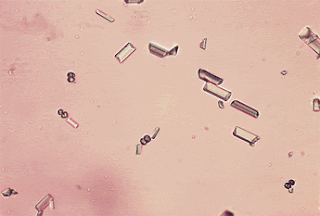
Kristal
Asam urat
Asam urat,
suatu produk metabolisme dari pemecahan protein, ada di urin dalam konsentrasi
yang tinggi dan umumnya menghasilkan berbagai macam struktur kristal.
Amorf urate dapat digambarkan sebagai granular, birefringent,
kristal tidak berwarna sampai kuning mereka tampak sebagai butiran
halus ketika diamati dengan pembesaran 10 x atau 40 × ( Gambar 5.
). Kristal ini sering terjadi ketika urin didinginkan. Kristal ini
membentuk sedimen warna merah muda di bagian bawah tabung centrifuge.
Kebanyakan amorf urate larut ketika ditambahkan larutan alkali ke
sedimen atau bila urin dihangatkan setelah pendinginan.
GAMBAR
5. Kristal
Amorf urat dalam urin. ( mikroskop cahaya, × 160.)
Kristal asam
urat adalah pleomorfik dibanding semua kristal urin, mereka ada
dalam berbagai bentuk, seperti batang, kubus ( Gambar 6. ), mawar enam
sisi, piring, rhombi, dan seperti batu asahan. Mereka sangat birefringent dan
bervariasi dalam ukuran. Kristal asam urat larut dalam
larutan alkali dan tidak larut dalam asam. Mereka biasanya tidak berwarna
sampai berwarna kuning pucat, pink atau coklat. Kristal asam
urat sering dikaitkan dengan batu ginjal, tetapi keberadaan mereka di urin
orang normal adalah sangat umum.
GAMBAR
,6. Kristal asam
urat (panah) dan sel skuamosa. Dalam gambar, kristal urat bentuk genjang
(a) dan tampak anisotropism di bawah sinar terpolarisasi (B). (mikroskop
cahaya, × 80)
Dalam garam
asam urat mungkin membentuk kristal lain , yaitu natrium
dan kalium urate. Hal ini dapat dilihat sebagai tidak
berwarna, berbentuk kristal jarum dan spherules kecoklatan. Penambahan setetes
asam asetat glasial menunjukkan hasil spheroids
Kalsium
Oksalat
Kristal
kalsium oksalat yang paling sering diamati pada urine asam
dan netral ( Gambar 7. ). Varian yang umum adalah
bentuk dihidrat, sebuah oktahedral, kristal berwarna mirip bentuk amplop.
Kristal jenis ini ditemukan dalam urin normal,
terutama setelah menelan asam askorbat dalam dosis besar atau makanan yang kaya
akan asam oksalat seperti tomat atau asparagus. Bentuk lainnya adalah
monohidrat, berbentuk seperti halter atau elips tergantung pada
apakah posisi datar atau miring ( Gambar. 8 ).
GAMBAR ,7. Kristal
kalsium oksalat , bentuk dihidrat. berbentuk persegi seperti
"bintang," atau "envelope ", penampilan yang khas. (
mikroskop cahaya, × 160.)
GAMBAR .8,.
Kristal
kalsium oksalat, bentuk monohidrat. Catatan penampilan oval ketika berbaring
datar, bentuk halter ketika miring. Dari urin pasien penyakit
kuning. ( mikroskop cahaya, × 160.)
Kristal Asam
Hippuric
Kristal asam
hippuric terkait dengan pH netral. Kristal ini biasanya
tidak berwarna, prisma memanjang dengan ujung piramida,
juga bisa tipis dan berbentuk jarum. Mereka birefringent dan
terkait dengan diet tinggi buah-buahan dan sayuran yang mengandung sejumlah
besar asam benzoat
Kristal
Amorf Fosfat
Kristal
fosfat adalah kristal yang paling sering diamati terkait dengan
urin alkali. Yang paling sering dijumpai adalah kristal amorf fosfat., ini
tidak dapat dibedakan dari kristal amorf urat dalam urin asam.
Kristal menghasilkan endapan putih di dasar tabung
centrifuge. .
Kristal
Triple Fosfat
Triple
fosfat (amonium-magnesium fosfat) adalah kristal birefringent
bentuknya mirip sebuah "peti mati-tertutup" ( Gambar 9 ),
birefringent dan sangat bervariasi dalam ukuran. Kristal juga dapat
ditemukan dalam urin netral dan larut dalam asam asetat.
GAMBAR
.9. kristal
Fosfat Triple dalam urin dengan latar belakang Gips hialin (panah)
. ( mikroskop cahaya, × 160)
Kadang-kadang
ditemukan dalam urin basa biasanya berbentuk "bintang"
Kristal
Amonium Biurate
Kristal
Amonium biurate memiliki bentuk "duri apel" (
Gambar 10. ) Berwarna coklat kekuningan dan sering menunjukkan striations
radial atau konsentris di pusat seperti "senjata" atau
spikula. Mereka biasanya ditemukan di dalam urin dengan pH netral dan larut
dalam natrium hidroksida. Mereka jarang ditemui pada urin normal.
GAMBAR
10. kristal
Amonium biurate dalam urin.Berbentuk "kepiting ",
spiculated kristal merupakan ciri khas dan berkaitan dengan urin alkali.
( mikroskop cahaya, × 400.)
Kristal
Kalsium Karbonat
kristal
karbonat kalsium berbentuk spherules-halter kecil ditemukan
dalam urin basa ( Gambar. 11 ). Karena ukurannya yang kecil, mereka
sering disangka bakteri. Bakteri tidak birefringent. Kristal-kristal
larut dalam asam asetat .
Gambar
11)
berbentuk halter kalsium karbonat. Kristal yang ditampilkan di sini dengan
kristal triple fosfat kecil (mikroskop, × 160.
CAST
Didefinisikan sebagai struktur mikroskopis silinder yang terbentuk di nefron
distal dan terjadi dalam urin normal ataupun bila ada penyakit.
Protein spesifik ini berbentuk "silinder"
yang diproduksi hanya di tubulus distal dan duktus
colleductus nefron, protein ini larut dan membentuk pita
protein tipis yang kemudian menyatu atau menjadi gips. Dalam
keadaan normal, hanya ada dua varietas gips muncul dalam sedimen urin: hialin
gips dan granular cast. Setiap bentuk baru harus dianggap "abnormal"
dan terkait dengan penyakit ginjal metabolik umum atau intrinsik. Setiap jenis
dibahas secara terpisah.
TABEL
.3. KLASIFIKASI CAST
Aselular
Cellular
Normal
Normal
Hening
Tak satupun
Granular
Tak satupun
Abnormal
Abnormal
Hening
Sel darah merah
Granular
Leukosit
Lunak
Epitel (RTE)
Pigmen
Lemak /
lemak tubuh oval
Berlemak
Bakteri /
jamur
RBC, sel-sel
darah merah, WBC, sel darah putih; RTE, epitel tubular ginjal.
Pada orang
normal, sejumlah kecil hialin atau granular satu atau dua per
10 LP (obyektif 10 x) pada urin sering ditemukan dan tidak selalu
berarti terkena penyakit ginjal. Kedua bentuk gips memiliki indeks bias
rendah dan karena itu agak sulit untuk dilihat dengan mikroskop cahaya biasa
kecuali kontras ditingkatkan. Menutup diafragma iris sambil menurunkan
kondensor dan mengatur intensitas cahaya akan menghasilkan kontras
yang optimal untuk pengamatan. Scan slide mikroskopik secara
menyeluruh untuk menemukan adanya Hialin atau Granular, dan jika ditemukan,
lakukan identifikasi dengan menggunakan lensa 40
×.
Cast hialin
Ini adalah
yang paling sering diamati dalam urin. Bentuknya yang transparan (indeks bias
yang rendah) menyebabkan agak sulit untuk dilihat. Bila diteliti tampak
perimeter luar halus dan sebuah matrik yang halus atau bergelombang
( Gambar .12. ) Sesekali butiran inklusi mungkin ada
dalam matriks, dan kadang-kadang sel satu atau dua juga mungkin terlihat. Cor
mungkin memiliki bentuk "ekor" atau titik.
Di
masa lalu, gip dengan ekor disebut cylindroid, istilah ini
dianggap kuno dan tidak umum digunakan saat ini ( Gambar 13. ).
GAMBAR
.12. Hialin cast, struktur protein bening (panah) sering
ditemukan pada sedimen urin normal
GAMBAR
13. Urine cylindroid, gip hialin dengan ekor. Cylindroid,
istilah kuno. ( mikroskop, × 160.)
Ketika
seorang pasien mengalami stres fisik atau emosional dalam 24 jam sebelumnya,
ditemukannya cylindruria tidak harus dianggap patologis., jika situasi stres
atau latihan fisik telah berhenti urin kembali ke keadaan normal dalam
waktu 24 hingga 48 jam
Granular
Cast
Cast ini
juga dapat diamati dalam jumlah meningkat di urin jika pasien telah terlibat
dalam situasi stres emosional atau telah menjalani latihan fisik berat
Dibandingkan dengan gips hialin, granular gips ditemukan dalam
rasio sekitar empat hialin per satu granular. Pada penghentian stres atau
latihan, jumlah butiran gips di urin kembali normal dalam waktu 24 hingga 48
jam. Alasan peningkatan produksi terkait stres atau latihan tidak diketahui.
Juga tidak diketahui alasan mengapa granular gips kadang muncul dalam urin
pasien pada pola makan yang kaya karbohidrat.
Granular
memiliki indeks bias lebih tinggi daripada hialin dan karena
itu lebih mudah ditemukan. Mereka juga silindris, walaupun beberapa
mungkin memiliki "ekor," dan memiliki perimeter. Umumnya, pada
orang normal, butir menutupi permukaan cor kecil dan teratur ( Gambar. 14
). Asal-usul butiran dalam orang normal sebagian berasal dari
partikel lisosomal intraseluler yang dikeluarkan ke dalam urin sebagai
produk metabolik dari epitel tubular ginjal . Ketika dalam aliran urin,
butiran lisosomal masuk ke dalam matriks cast hialin
dan dengan demikian mengubah dari yang sebelumnya mulus ( cast hialin)
menjadi kasar (cast granular).
.
GAMBAR
,14. Granular cast Dalam contoh yang ditunjukkan di sini (panah),
butiran-butiran tidak menutupi seluruh permukaan cor tetapi relatif merata. (
mikroskop cahaya, × 160.)